Understanding Sentiment, Emotion and its Intensity by Analysing Meme Images
In this post, I want to introduce a new topic which is took place at First Workshop on Multimodal Fact-Checking and Hate Speech Detection in AAAI 2022. And I got the 1st position on the leaderboard of this challenge. Link to the challenge: https://aiisc.ai/defactify/memotion_2.html
1. Abstract
In this post, I want to talk about Meme Analysis which is about explaining its Sentiment, Emotion and Intensity.
The growing ubiquity of Internet memes on social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter further suggests that we can not ignore such multimodal content (vision and language) anymore. To the best of our knowledge, there is not much attention towards meme emotion, and sentiment analysis.
The task of Memotion analysis consists of three task (1) sentiment(positive, negative, neutral) classification, (2) emotion (sarcastic,funny,offensive, motivation) classification and (3) their corresponding intensity.
Here is some example of Meme Images, they contain two information simultaneously which is text and image:

2. Model
The models consist of 3 primary types which are Unimodal for Only Text, Unimodal for Only Image, Multimodal for Text and Image.
In the Multimodal, I also employed several fusion mechanism such as Concatenation, Multihop Attention, and Stacked Attention.
2.1 Unimodal for Text
BERT and its variant, e.g., RoBERTa, are widely used in Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks and have demonstrated as efficient methods. In this competition, we employed them for three subtasks. In subtasks A and B, a RoBERTa is used while in subtask C, four RoBERTa models are adopted so that every backbone corresponds classifying the intensity of each emotion.
2.2 Unimodal for Image
As a vision-based approach, EfficientNet-v2 is a well-known backbone with respect to speedy inference and a low number of parameters. In three subtasks, EfficientNet-v2 is used as an extractor to create embeddings. Subtask A has one classification branch to deal with three sentiment types while subtasks B and C have four branches which each is responsible for classifying four types of emotions as well as their intensity.
2.3 Multimodal
Multi-modality is to aggregate vision and text to obtain correlated information. In this challenge, we build three different fusion models including concatenation, multi-hop attention, and stacked attention network.
2.3.1 Concatenation
Traditionally, concatenation of two feature vectors, a.k.a two modalities, has been a typical solution to obtain aggregated features. However, the method does not take into account the importance of each word that is within corresponding regions of the image.
2.3.2 Multi-hop Attention
Multi-hop attention focuses parts of a given image together with texts within it. The technique aims to emphasize dissimilar features between image regions and textual utterances by defining a relevant matrix $R$, which is the cosine distance between textual and visual features.
2.3.3 Stacked Attention
While a multi-hop attention network is used to learn attention maps between an image and texts within it, a stacked attention network has a capability of learning an attention map in multiple times. Through such attention layers, interested regions are promoted through a referred concept within a given sentence.
3. Techniques
In this competition, I have used some techniques to improve the F1 scores of the model.
3.1 Scence Text Detection
Although both textual and visual features are important for meme emotion analysis, there is little correlation between them in the MEMOTION 2.0 dataset. Besides, the caption is also provided as a part of the dataset. Therefore, in this study, the text is removed from the image before extracting and training the proposed model.
Based on the previous works that summarized both traditional and deep learning approaches for text detection and recognition, we design a preprocessing scheme to remove texts from images as follows. First, we employ the EAST module to detect all text regions in an image. Then these regions are removed from the image, and we use the output image as the input for EfficientNet-v2 in the proposed framework.

3.2 Auto Augmentation
Augmentation is a simple but important technique to increase the size of a given dataset, leading to a better generalization of a training model. However, current data augmentation is based on a set of manually designed algorithms such as Crop, Rotation, and Resize. In our experiment, we adopt the Auto Augment technique which uses reinforcement learning to automatically search for a better data augmentation strategy.
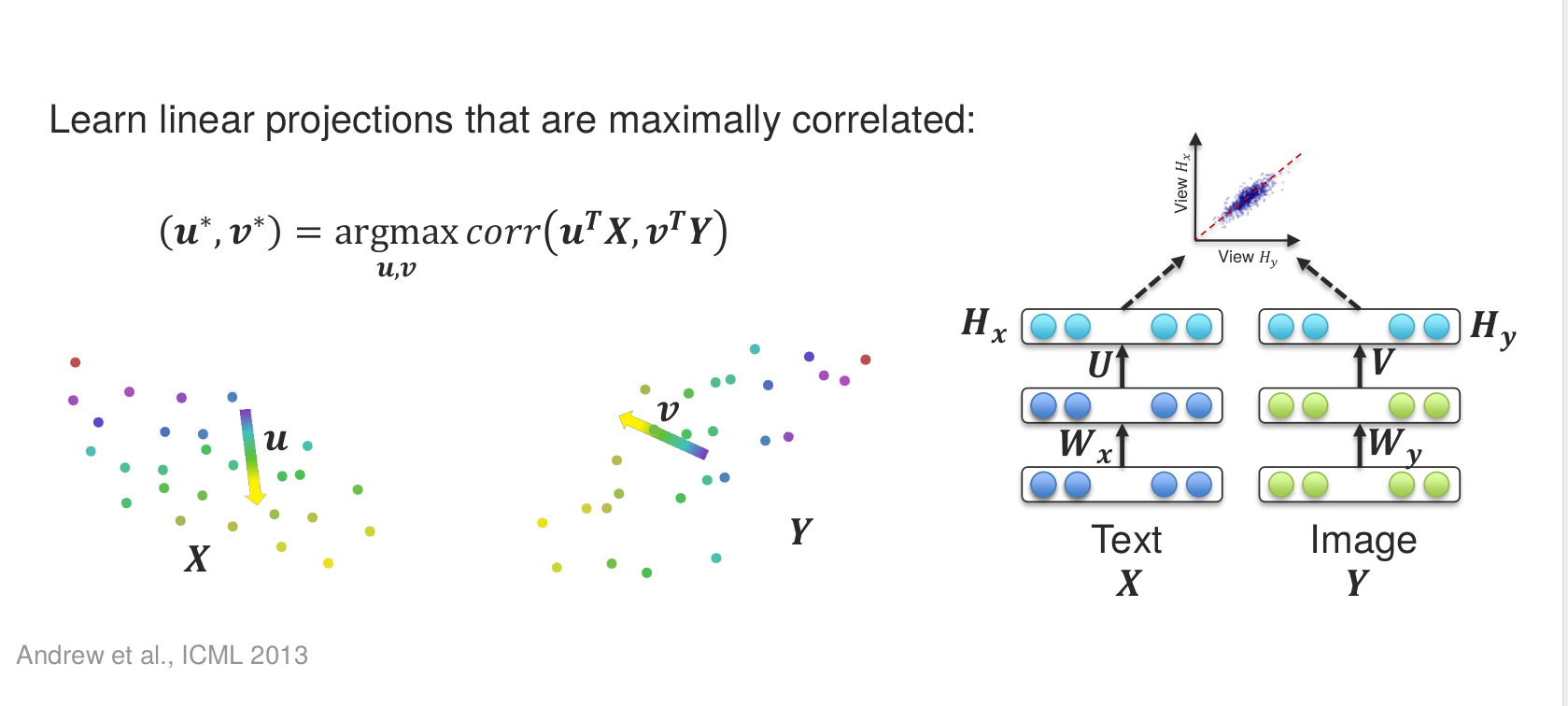
3.3 Canonical Correlation Analysis
The Canonical correlation analysis (CCA) is based on a well-established statistical technique that searches for a linear combination of input vectors by maximizing their correlations. Deep CCA tries to utilize the power of both deep neural networks and CCA to overcome projection constraints of CCA . In this study, correlation scores obtained from Deep CCA is included to our loss function to maximize the correlation between two features, leading to a higher classification rate.
3.4 Loss function, Optimizer, etc
For the classification task, I use CrossEntropy typically, but I also tested on Training Signal Anealing CrossEntropy which is a loss function that helps mitigate the imbalance effect of the dataset.
In terms of Optimizer, I tried several ones such as Adam, SGD, AdamW, LookAHead, etc.
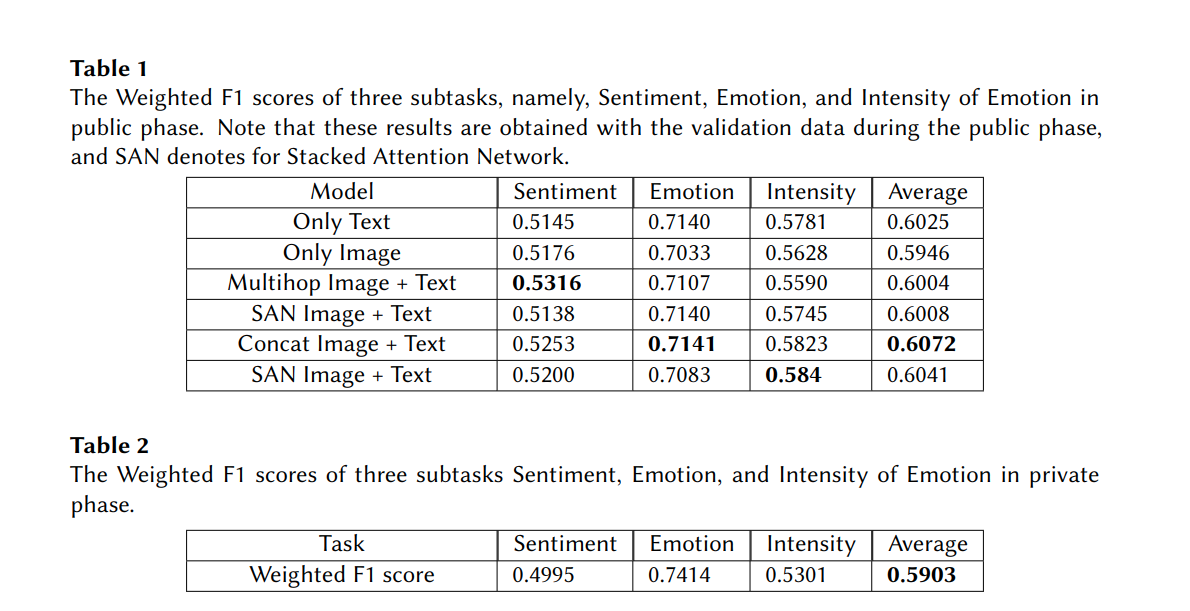
4. Result
5. Application
Analysis meme images can help social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter mitigate the false information that are disemminating widely.
Moreover, the technique in this post can be applied to other Vision Language problems.
6. Code and Paper
Link code: Code
Link paper: Paper